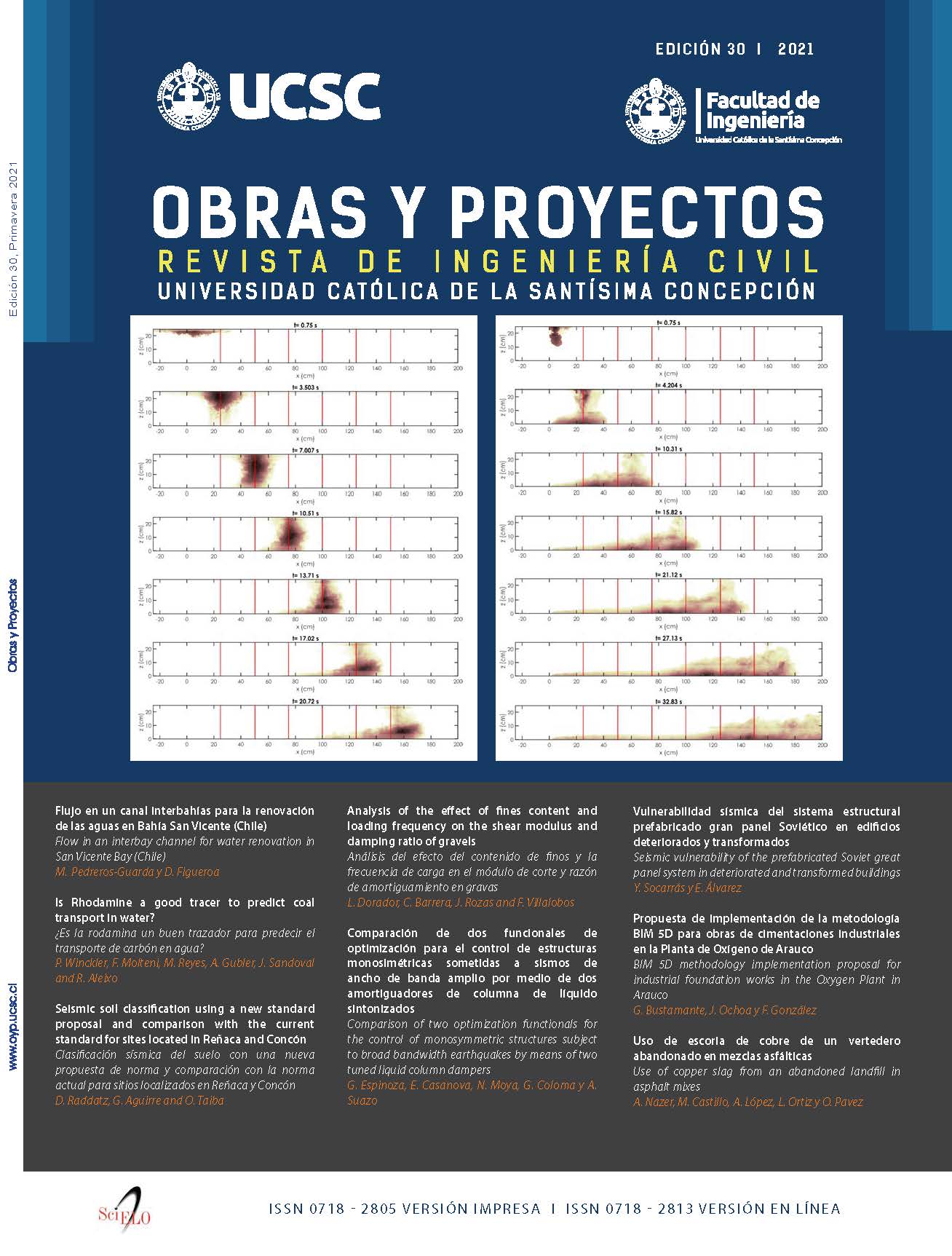
Is Rhodamine a good tracer to predict coal transport in water?
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-28132021000200016Keywords:
Coal, Rhodamine, Advection, Turbulent diffusion, Image processingAbstract
A simple and low-cost experimental procedure to compare the mixing and transport of two substances in water is presented in this paper, aiming to investigate if rhodamine can predict the fate of coal transport in water. The procedure is based on acoustic Doppler techniques to characterize the flow and imaging techniques to measure the transport of substances discharged from an instantaneous point source near the free surface. To validate this procedure, several tests are carried out for rhodamine and two subsamples of coal (defined by a fine and coarse granulometry) in a flume under currents. The results show that the mixing of rhodamine resembles the finest fraction of coal that is transported as a suspended material, but fails to characterize the larger coal grains that experience sedimentation. The procedure here proposed can be expanded to characterize the mixing of substances in a body of water under other conditions, such as waves or wind driven currents.
References
Abessi, O. and Roberts, P.J.W. (2014). Multiport diffusers for dense discharges. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 140(8), 04014032.
Abessi, O. and Roberts, P.J.W. (2015). Dense jet discharges in shallow water. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 142(1), 04015033.
Ahrens, M.J. and Morrisey, D.J. (2005). Biological effects of unburnt coal in the marine environment. Oceanography and Marine Biology: An Annual Review, Gibson, R.N., Atkinson R.J.A., and Gordon, J.D.M. (eds.), Taylor and Francis, 43, 69-122.
ASTM (2005). Standard test method for sieve analysis of fine and coarse aggregates. ASTM C136-05, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, USA.
Bennett, J.R. (1987). The physics of sediment transport, resuspension, and deposition. Hydrobiologia 149(1), 5-12.
Berry, K.L., Hoogenboom, M.O., Flores, F. and Negri, A.P. (2016). Simulated coal spill causes mortality and growth inhibition in tropical marine organisms. Scientific Reports 6(1), 1-8.
Choi, K.W., Lai, C.C. and Lee, J.H. (2015). Mixing in the intermediate field of dense jets in cross currents. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 142(1), 04015041.
Clark, D.B., Lenain, L., Feddersen, F., Boss, E. and Guza, R.T. (2014). Aerial imaging of fluorescent dye in the near shore. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology 31(6):1410-1421.
Coleman, N.L. (1970). Flume studies of the sediment transfer coefficient. Water Resources Research 6(3), 801-809.
Daviero, G.J. and Roberts, P.J.W. (2006). Marine wastewater discharges from multiport diffusers. III: Stratified stationary water. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 132(4), 404-410.
Dey, S. (2014). Fluvial hydrodynamics. Springer, Berlin, Germany.
Dietrich, W.E. (1982). Settling velocity of natural particles. Water Resources Research 18(6), 1615-1626.
Fischer, H.B., List, J.E., Koh, C.R., Imberger, J. and Brooks, N.H. (2013). Mixing in inland and coastal waters. Elsevier.
Franco-Herrera, A., Grijalba-Bendeck, L.M., Ibáñez, J.P. y Daza, J.N. (2011). Carbón, clima, playas y peces: el caso de la zona costera del departamento del Magdalena. Editorial Tadeo Lozano, Bogotá, Colombia.
Goring, D.G. and Nikora, V.I. (2002). Despiking acoustic Doppler velocimeter data. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 128(1), 117-126.
Graf, W.H. and Cellino, M. (2002). Suspension flows in open channels; experimental study. Journal of Hydraulic Research 40(4), 435-447.
Gualtieri, C., Angeloudis, A., Bombardelli, F., Jha, S. and Stoesser, T. (2017). On the values for the turbulent Schmidt number in environmental flows. Fluids 2(2), 17.
Gungor, E. and Roberts, P.J.W. (2009). Experimental studies on vertical dense jets in a flowing current. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 135(11), 935-948.
Hughes, S.A. (1993). Physical models and laboratory techniques in coastal engineering. Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering, Volume 7. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore.
IEA (2011). World energy outlook. International Energy Agency, Paris, France.
James, I.D. (2002). Modelling pollution dispersion, the ecosystem and water quality in coastal waters: a review. Environmental Modelling & Software 17(4), 363-385.
Jha, S.K. and Bombardelli, F.A. (2010). Toward two‐phase flow modeling of nondilute sediment transport in open channels. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface 115(F3), F03015.
Johnson, R. and Bustin, R.M. (2006). Coal dust dispersal around a marine coal terminal (1977–1999), British Columbia: The fate of coal dust in the marine environment. International Journal of Coal Geology 68(1-2), 57-69.
Julien, P.Y. (2010). Erosion and sedimentation. Cambridge University Press, UK.
Klemas, V., Maurer, D., Leatham, W., Kinner, P. and Treasure, W. (1974). Dye and drogue studies of spoil disposal and oil dispersion. Journal (Water Pollution Control Federation) 46(8), 2026-2034.
Lin, J.F., Hsiao, S.C., Hsu, T.W. and Chang, K.A. (2012). Buoyancy effect on turbulent round jet under regular waves. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering 139(3), 190-208.
Moritz, H., Puckette, T., Marsh, J., Boudreau, R., Siipola, M. and Ott, M. (2011). Utilizing sediment tracer studies to evaluate transport pathways at the mouth of the Columbia River, USA. Coastal Sediments Specialty Conference, Miami, Florida, USA, 1565-1579.
Muste, M., Yu, K., Fujita, I. and Ettema, R. (2005). Two‐phase versus mixed‐flow perspective on suspended sediment transport in turbulent channel flows. Water Resources Research 41(10), W10402.
Roberts, P.J.W. and Tian, X. (2000). Three-dimensional imaging of stratified plume flows. 5th International Conference on Stratified Flows, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada.
Roberts, P.J.W. and Tian, X. (2004). New experimental techniques for validation of marine discharge models. Environmental Modelling and Software 19(7-8), 691-699.
Roberts, P.J.W., Tian, X. and Jung, Y. (2011). Physical model study of an alternating diffuser for thermal discharge. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 137(9), 1027-1036.
Rossi, V., Ser‐Giacomi, E., López, C. and Hernández‐García, E. (2014). Hydrodynamic provinces and oceanic connectivity from a transport network help designing marine reserves. Geophysical Research Letters 41(8), 2883-2891.
Rouse, H. (1937). Modern conceptions of the mechanics of fluid turbulence. Transactions of the ASCE 102(1), 463-505.
Royal Haskoning (2016a). Swansea channel sand tracing. Final Report. Elaborated for NSW Department of Primary Industries (Lands). Australia.
Royal Haskoning (2016b). Old bar beach sediment tracing. Final Report. Elaborated for Greater Taree City Council. Australia.
Rypina, I.I., Kirincich, A. and Peacock, T. (2021). Horizontal and vertical spreading of dye in the coastal ocean of the northern Mid-Atlantic bight. Continental Shelf Research 230, 104567.
Schweinfurth, S.P. (2009). An introduction to coal quality. The National Coal Resource Assessment Overview, Pierce, B.S. and Dennen, K.O. eds., US Geological Survey Professional Paper 1625–F, Chapter C, Virginia, USA.
Smith, S.J., Marsh, J. and Puckette, T. (2007). Analysis of fluorescent sediment tracer for evaluating nearshore placement of dredged material. XVIII World Dredging Congress, Randell, R.E. (ed.), Florida, USA, 1345-1358.
Takewaka, S., Misaki, S. and Nakamura, T. (2003). Dye diffusion experiment in a longshore current field. Coastal Engineering Journal 45(3), 471-487.
Tang, L., Sheng, J., Hatcher, B.G. and Sale, P.F. (2006). Numerical study of circulation, dispersion, and hydrodynamic connectivity of surface waters on the Belize shelf. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 111(C1), C01003.
Tian, X., Roberts, P.J.W. and Daviero, G.J. (2004a). Marine wastewater discharges from multiport diffusers. I: Unstratified stationary water. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 130(12), 1137-1146.
Tian, X., Roberts, P.J.W. and Daviero, G.J. (2004b). Marine wastewater discharges from multiport diffusers. II: Unstratified flowing water. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 130(12), 1147-1155.
Tian, X., Roberts, P.J.W. and Daviero, G.J. (2006). Marine wastewater discharges from multiport diffusers. IV: Stratified flowing water. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 132(4), 411-419.
Tropea, C. and Yarin, A.L. (2007). Springer handbook of experimental fluid mechanics. Springer Science and Business Media.
Vanoni, V.A. (1975). Sediment discharge formulas. Sedimentation Engineering, ASCE, Manual and Reports on Engineering Practice 54, 190-229.
Vroom, J., van Maren, B., Marsh, J. and van der Lelij, A.C. (2017). Effectiveness of the mud motor near Koehool. Results and interpretion of a tracer study. Deltares, Delft, the Netherlands.
WCA (2020). Coal and electricity. World Coal Association. https://www.worldcoal.org/coal/uses-coal/coal-electricity (5/14/2020).
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.