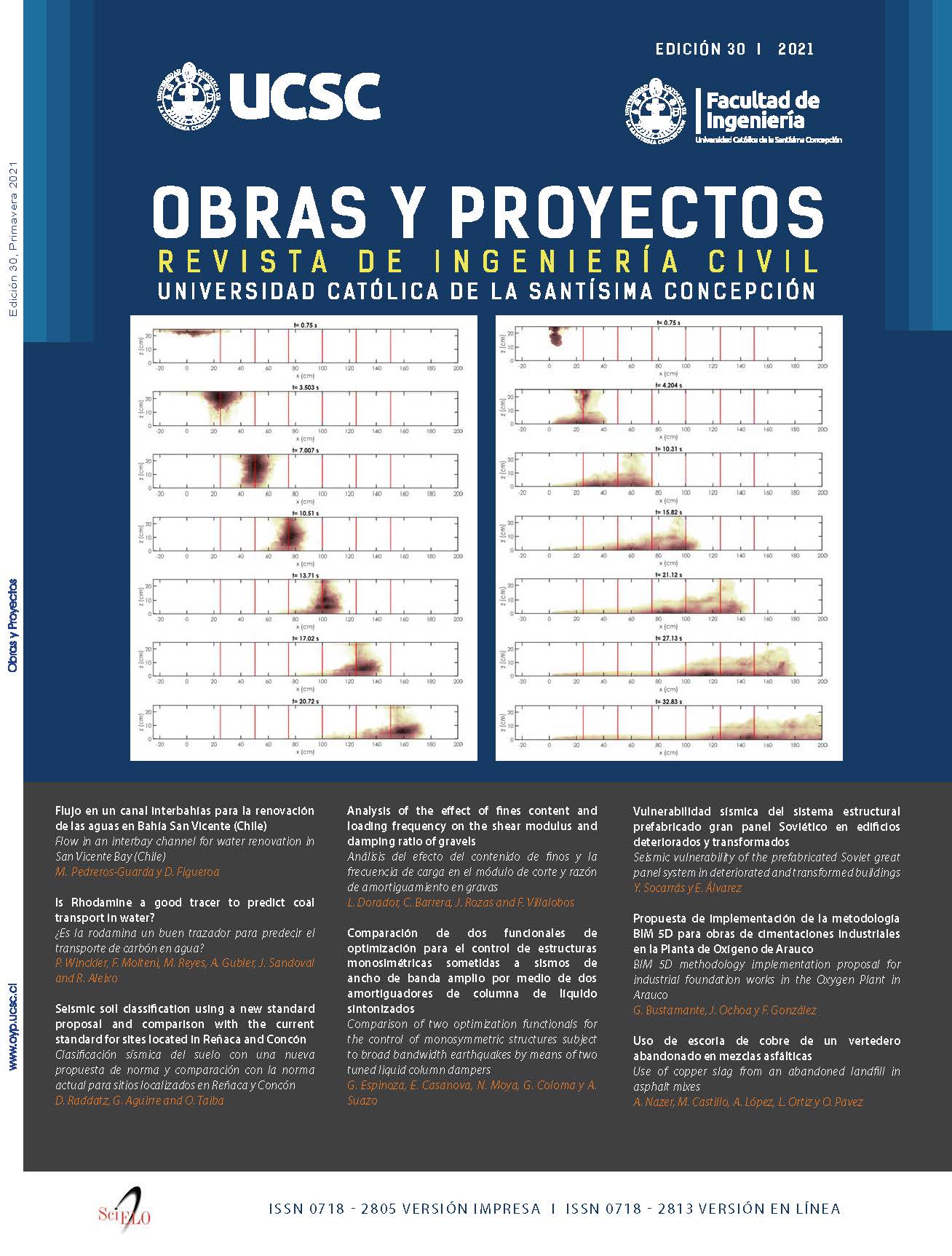
Comparación de dos funcionales de optimización para el control de estructuras monosimétricas sometidas a sismos de ancho de banda amplio por medio de dos amortiguadores de columna de líquido sintonizados
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-28132021000200050Palabras clave:
Amortiguador de columna de líquido sintonizado, Optimización, Balance torsional, Análisis estocásticoResumen
En este trabajo se estudia el comportamiento de dos amortiguadores de columna de líquido sintonizados (ACLS), en el control torsional de una estructura asimétrica de comportamiento lineal, ante una excitación sísmica de alto contenido de frecuencias. El modelo de estudio es una estructura monosimétrica en dirección X a la que se le han adicionado dos ACLS en dirección Y, para controlar el movimiento de la estructura con acoplamiento lateral-torsional. Se consideran dos criterios de optimización, cada uno representando una forma alternativa de determinar la demanda de deformación de los bordes de la planta. El primer criterio consiste en igualar las varianzas de deformación de los bordes de la planta. El segundo criterio consiste en igualar las desviaciones estándar de deformación de los bordes de la planta. El objetivo final es balancear torsionalmente la estructura. Los resultados muestran un balance torsional prácticamente idéntico, con los ACLS optimizados con cada uno de los criterios, a excepción del caso de una razón de frecuencia torsional flexible y una razón de masa baja. Además, se encuentra que la posición óptima de los ACLS para excentricidades mayores a 0.12, sigue la misma regla de comportamiento de la posición óptima de los amortiguadores de masa sintonizados.
Referencias
Almazán, J.L. and de la Llera, J.C. (2009). Torsional balance as new design criterion for asymmetric structures with energy dissipation devices. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics 38(12), 1421-1440.
Almazán, J.L., Espinoza, G. and Aguirre, J.J. (2012). Torsional balance of asymmetric structures by means of tuned mass dampers. Engineering Structures 42, 308-328.
Chakraborty, S., Debbarma, R. and Marano, G.C. (2012). Performance of tuned liquid column dampers considering maximum liquid motion in seismic vibration control of structures. Journal of Sound and Vibration 331(7), 1519–1531.
Clough, R.W. and Penzien, J. (1975). Dynamics of structures. 2nd edition, McGraw-Hill, USA.
de la Llera, J.C., Almazán, J.L. and Vial, I.J. (2005). Torsional balance of plan‐asymmetric structures with frictional dampers: analytical results. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics 34(9), 1089-1108.
Espinoza, G., Carrillo, C. and Suazo, A. (2018a). Analysis of a tuned liquid column damper in non-linear structures subjected to seismic excitations. Latin American Journal of Solids and Structures 15(7), e91.
Espinoza, G., Neira, D. y Cifuentes, A. (2018b). Análisis de un amortiguador de masa sintonizado óptimo en estructuras asimétricas no lineales. Obras y Proyectos 23, 39-54.
Espinoza, G., Almazán, J.L., Jara, C. and Benedetti, F. (2019). Torsional balance of nonlinear asymmetrical structures by means of a tuned mass damper. Structural Control and Health Monitoring 26(11), e2442.
García, M., de la Llera, J.C., Almazán, J.L. (2007). Torsional balance of asymmetric structures with viscoelastic dampers. Engineering Structures 29(6): 914-932.
NCh2745 (2013). Análisis y diseño de edificios con aislación sísmica. Instituto Nacional de Normalización INN, Santiago, Chile.
Roberts, J.B. and Spanos, P.D. (2003). Random vibration and statistical linearization. Dover Publications, New York, USA.
Rozas, L., Boroschek, R.L., Tamburrino, A. and Rojas, M. (2016). A bidirectional tuned liquid column damper for reducing the seismic response of buildings. Structural Control and Health Monitoring 23(4), 621–640.
Saitua, F., Lopez-Garcia, D. and Taflanidis, A.A. (2018). Optimization of height-wise damper distributions considering practical design issues. Engineering Structures 173,768-786.
Sakai, F., Takaeda, S. and Tamaki, T. (1989). Tuned liquid column damper - New type device for suppression of building vibrations. First International Conference on High-Rise Buildings, Nanjing, China, 926-931.
Seguín, C.E., Almazán, J.L. and de la Llera, J.C. (2013). Torsional balance of seismically isolated asymmetric structures. Engineering Structures 46, 703-717.
Sgobba, S. and Marano, G.C. (2010). Optimum design of linear tuned mass dampers for structures with nonlinear behaviour. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 26(6), 1739-1755.
Shum, K.M. (2009). Closed form optimal solution of a tuned liquid column damper for suppressing harmonic vibration of structures. Engineering Structures 31(1), 84-92.
Shum, K.M. and Xu, Y.L. (2002). Multiple-tuned liquid column dampers for torsional vibration control of structures: experimental investigation. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics 31(4), 977-991.
Won, A.Y., Pires, J.A. and Haroun, M.A. (1996). Stochastic seismic performance evaluation of tuned liquid column dampers. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics 25(11), 1259-1274.
Yalla, S.K. and Kareem, A. (2000). Optimum absorber parameters for tuned liquid column dampers. Journal of Structural Engineering 126(8), 906–915.
Descargas
Publicado
Número
Sección
Licencia

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial 4.0.